The World Wide Web, or simply the web, has fundamentally transformed the way we live, work, and play. In just a few short decades, the web has gone from a basic static platform for publishing information to a dynamic, interactive network that has revolutionized the way we access information, communicate with each other, and conduct business.
The web has allowed us to access information on virtually any topic from anywhere in the world, at any time. This has opened up new opportunities for learning, research, and discovery, and has enabled us to stay connected with friends and family across the globe. The web has also transformed the way we communicate with each other, providing us with new tools and platforms to connect and collaborate, whether for personal or professional purposes.
One of the most significant impacts of the web has been on the world of business. The rise of e-commerce has transformed the way we shop and do business, providing us with access to a vast range of products and services, and enabling us to conduct transactions with just a few clicks. The web has also created new opportunities for entrepreneurs and startups, allowing them to reach new markets and customers in ways that were once impossible.
Over the years, the web has gone through several iterations, each with its unique features and capabilities. Web1, or the static web, was the first iteration of the World Wide Web and was focused primarily on creating a global repository of information. Web2, or the social web, introduced interactivity, user-generated content, and social networking, transforming the way we use the internet. Web3, or the decentralized web, is the most recent iteration of the World Wide Web, and is a vision for a more decentralized and secure internet, built on blockchain technology.
Each iteration of the web has brought new capabilities and opportunities, creating new ways to access information, connect with each other, and conduct business. With each new iteration, the web has become more sophisticated, more dynamic, and more interactive, creating new possibilities and new challenges for the digital world.
In this article, we will explore these iterations in more detail and provide examples of their impact.
Exploring Web 1, Web2 and Web3
Web1
Web1, also known as the static web, emerged in the early 1990s and was the first iteration of the World Wide Web. It was primarily used for publishing static content such as HTML pages, text, and images. This iteration of the web was essentially a one-way communication system, where users could only consume content, but not contribute to it. Websites were mostly designed for desktop computers and were not optimized for mobile devices.
Examples of Web1
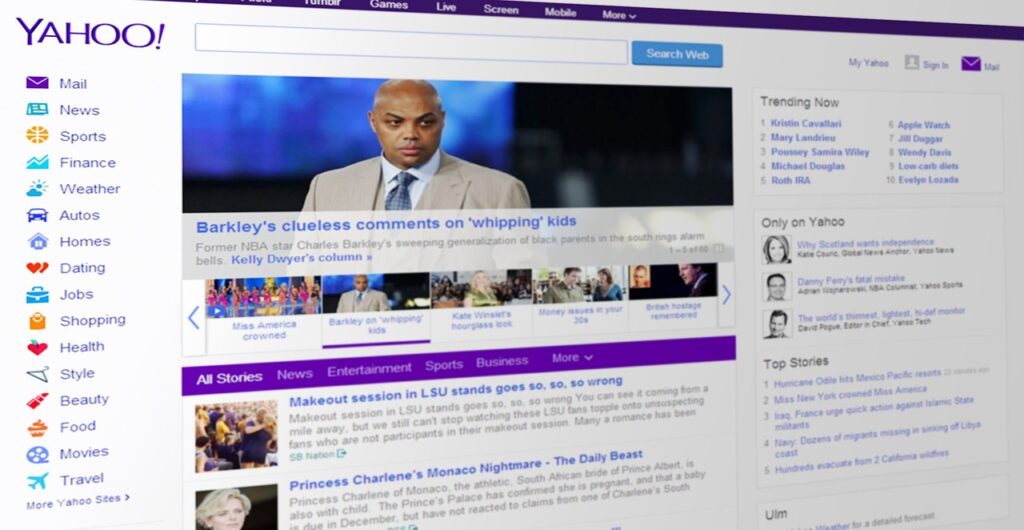
The primary goal of Web1 was to create a global repository of information, accessible to anyone with an internet connection. However, its limitations included a lack of interactivity, being heavily reliant on search engines for users to discover content, and the inability of users to contribute to the content. Examples of websites that were popular during the Web1 era include Yahoo!, AOL, and GeoCities.
Web2
Web2, also known as the social web, emerged in the mid-2000s and transformed the way we use the internet. This iteration of the web introduced interactivity, user-generated content, and social networking. Websites became more dynamic and responsive, and users could interact with each other, share information, and collaborate on projects.
Web2 brought about the rise of social media platforms, such as Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn, which enabled users to connect with each other on a global scale. Web2 also introduced cloud computing, which allowed users to store and access data from anywhere, at any time, using any device.
Examples of Web2
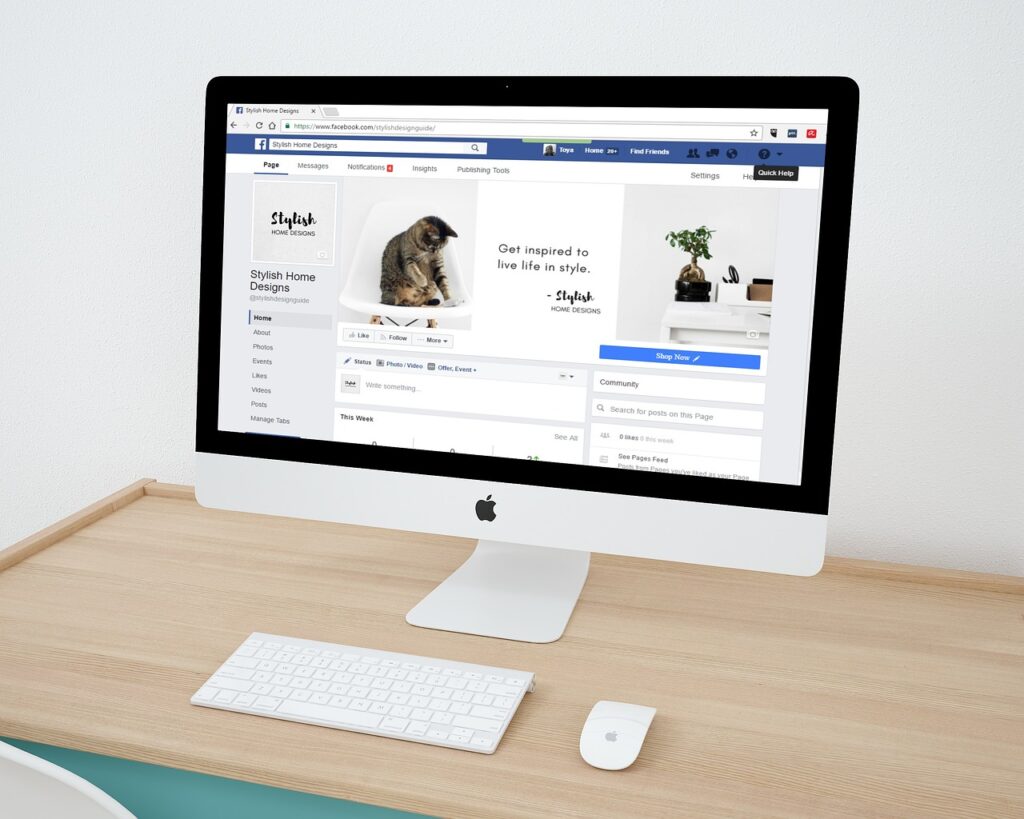
Web2’s impact on e-commerce was significant, as it paved the way for online marketplaces, such as Amazon and eBay. Web2 also transformed the way we consume media, with the rise of streaming platforms, such as Netflix and YouTube.
Web3
Web3, also known as the decentralized web or the blockchain web, is the most recent iteration of the World Wide Web. Web3 is still in its infancy and is a vision for a more decentralized and secure internet. Web3 aims to eliminate the centralization of power and data that Web2 has created by enabling users to own and control their data.
Web3 is built on blockchain technology, which is a distributed ledger that records transactions in a secure and transparent manner. Web3 enables users to transact with each other without the need for intermediaries, such as banks or social media platforms.
Web3’s impact on e-commerce could be significant, as it enables users to transact with each other directly, without the need for a centralized marketplace. Web3 also has the potential to transform the way we share and consume media, with the rise of decentralized content platforms.
Examples of Web3

Examples of Web3 technologies include cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, which allow users to transact without the need for banks or other financial institutions. Other examples include decentralized platforms such as IPFS (InterPlanetary File System) and the Solid platform, which enable users to store and share data without the need for centralized servers.
Impact of Each Iteration of the Web
While the article provides a basic understanding of each iteration of the web, more specific examples of their impact would help to illustrate their significance. For example, Web1 revolutionized the way we access information by making it available to anyone with an internet connection. This led to the rise of search engines like Google and Yahoo!, which enabled users to find information quickly and easily. Web2, on the other hand, transformed the way we communicate and collaborate online, leading to the rise of social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter. These platforms have fundamentally changed the way we interact with each other, enabling us to connect with people from all over the world and share information in real-time.
Web3 has the potential to transform the way we transact online, by enabling users to transact with each other directly without the need for intermediaries. This could lead to greater transparency and trust in online transactions, as well as greater control and ownership over our data. For example, decentralized marketplaces like OpenBazaar are already using Web3 technology to enable peer-to-peer transactions without the need for a centralized marketplace.
Drawbacks and Challenges of a Decentralized Web
While the potential benefits of a decentralized web are significant, there are also potential drawbacks and challenges to consider. One of the biggest challenges is scalability, as the decentralized nature of Web3 can make it more difficult to handle large amounts of data and transactions. Additionally, regulatory issues may arise as Web3 enables users to transact directly with each other without the need for intermediaries. This could create challenges for governments and regulatory bodies that rely on intermediaries to enforce laws and regulations.
Another potential challenge is the lack of standardization in Web3 technology, which can make it difficult for
developers and users to adopt and use the technology. This lack of standardization can also lead to compatibility issues between different Web3 applications and platforms, which can limit their overall effectiveness and impact.
Furthermore, the decentralized nature of Web3 can also make it more difficult to ensure security and protect against fraud and hacking. While the blockchain technology that underpins Web3 is inherently secure, there have been instances where hackers have exploited vulnerabilities in Web3 applications to steal cryptocurrency and other assets.
As Web3 technology continues to develop, it will be important for developers, regulators, and users to work together to address these challenges and ensure that the potential benefits of a decentralized web can be fully realized.
The Future of the Web: Web3 and the Potential for a Web4
The future of the web is full of exciting possibilities and potential transformations. As the web evolves, it is likely that we will see even more innovative and transformative use cases emerge. Web3 is still in its early stages of development, but experts predict that it could transform the way we interact with data and each other online. The decentralized nature of Web3 could provide users with greater control and ownership over their data, while enabling new forms of trust and transparency in online transactions. Some potential applications of Web3 include decentralized social media platforms, decentralized marketplaces, and even decentralized governance systems. As Web3 technology continues to evolve, we are likely to see even more innovative and transformative use cases emerge.
Looking even further ahead, some experts predict that we could see the emergence of a Web4 that is characterized by even greater levels of interconnectivity and intelligence. The Web4 could be powered by artificial intelligence, enabling the creation of more personalized and intelligent web experiences. Alternatively, we may see the emergence of a more immersive web, with the incorporation of virtual and augmented reality technologies. Whatever the future may hold, it is clear that the web will continue to transform the way we live, work, and communicate in ways that we cannot yet fully predict or imagine.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the World Wide Web has undergone several iterations since its inception, each with its unique features and capabilities. Web1, Web2, and Web3 have transformed the way we access information, communicate with each other, and conduct business. Web1 set the foundation for the modern web, Web2 introduced interactivity, user-generated content, and social networking, and Web3 has the potential to create a more decentralized and secure internet. As the web continues to evolve, we are likely to see even more innovative and transformative use cases emerge, such as decentralized social media platforms, decentralized marketplaces, and even decentralized governance systems. The possibility of a Web4 powered by artificial intelligence or augmented reality also adds to the excitement and potential of the future of the web. One thing is for sure – the web will continue to transform the way we live, work, and communicate in ways that we cannot yet fully predict or imagine.



